In networking, IP addresses are the backbone of communication between devices. Among these addresses, the 192.168.x.x range is commonly used for private networks. One specific address that occasionally appears in technical discussions is 192.168.l00.1. While it resembles the widely used 192.168.100.1, the subtle replacement of zero with a lowercase “L” can confuse users and administrators alike. This guide will explore everything you need to know about 192.168.l00.1, including access, configuration, troubleshooting, security, and advanced network management.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Private IP Addresses
- What is 192.168.l00.1?
- Accessing the 192.168.l00.1 Admin Panel
- Common Uses of 192.168.l00.1
- Troubleshooting 192.168.l00.1 Access Issues
- Advanced Configuration via 192.168.l00.1
- DHCP, NAT, and IP Management
- Router Firmware and Security Updates
- Case Studies: Practical Uses of 192.168.l00.1
- Best Practices for Network Security
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Private IP Addresses
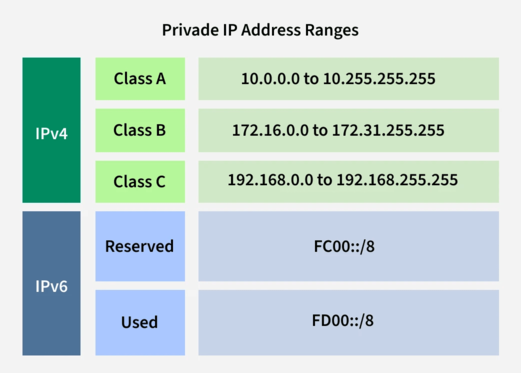
Private IP addresses are reserved addresses used within internal networks. They are not routable on the public internet and are typically used for:
- Home networks
- Office networks
- Corporate intranets
The 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 range is one of the most common private IP ranges. Devices within this range can communicate with each other directly, but require a router with NAT (Network Address Translation) to connect to external networks like the internet.
Understanding private IP addresses is essential for configuring and troubleshooting home or office networks efficiently.
2. What is 192.168.l00.1?
192.168.l00.1 is a local network IP address, often mentioned in router manuals and networking tutorials. Despite its unusual appearance—using a lowercase “L” instead of zero—it functions similarly to 192.168.100.1.
Key points about 192.168.l00.1:
- It is part of the private IPv4 address space.
- It is typically assigned as the default gateway for routers, enabling network management.
- It allows users to access the router’s admin panel for configuration purposes.
⚠️ Important: If your browser cannot connect to 192.168.l00.1, the device may actually use 192.168.100.1, or the IP may have been manually changed. Always verify the router’s default IP.
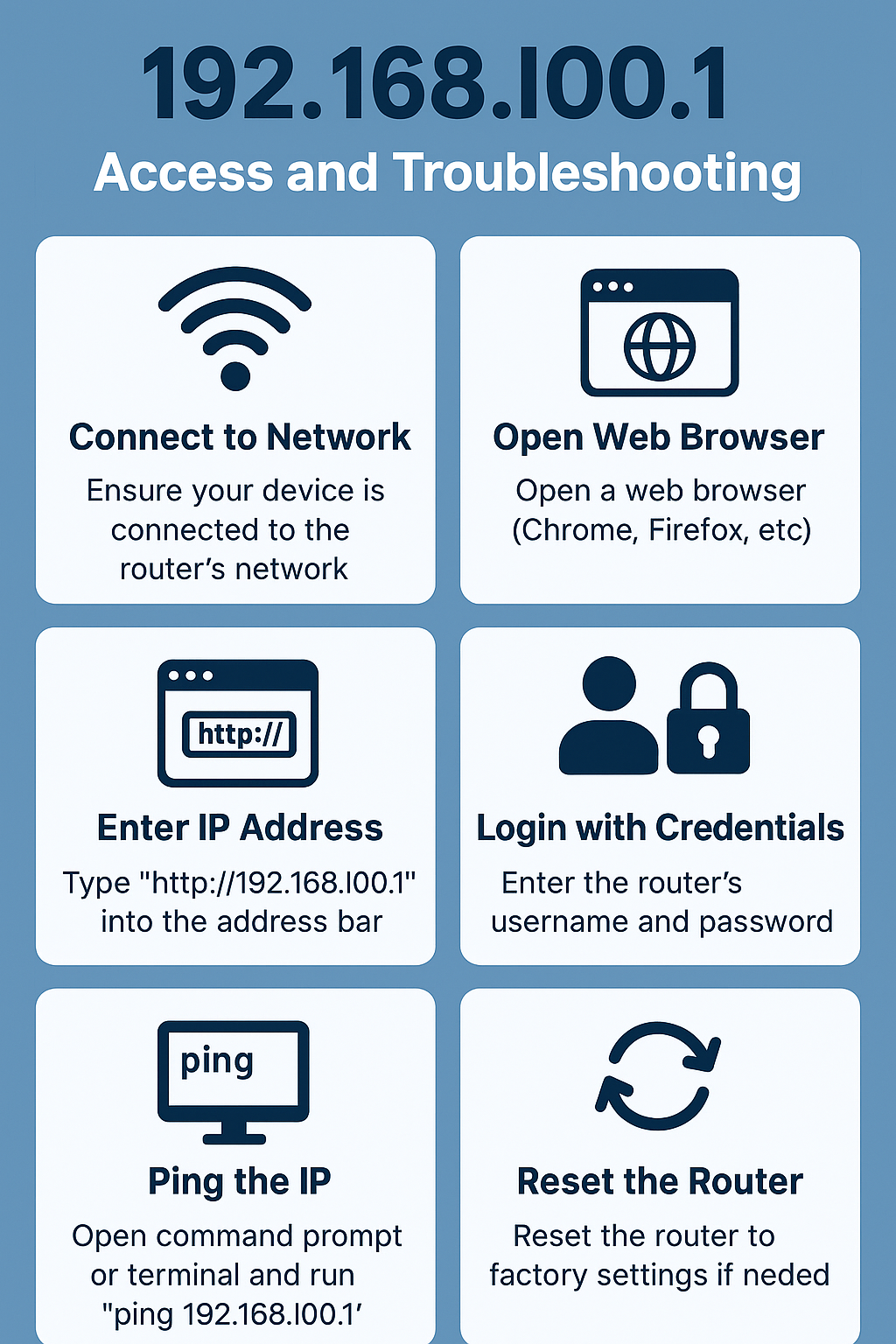
3. Accessing the 192.168.l00.1 Admin Panel
Accessing your router through 192.168.l00.1 allows you to configure essential network settings. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Connect to the Network
Ensure your device is connected via Wi-Fi or Ethernet to the router. Only devices on the same local network can access the router interface.
Step 2: Open a Web Browser
Use popular browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge.
Step 3: Enter the IP Address
Type http://192.168.l00.1 in the browser address bar and press Enter.
Step 4: Enter Login Credentials
Most routers require a username and password. Default combinations include:
| Username | Password |
|---|---|
| admin | admin |
| admin | password |
If login fails, consult your router’s manual or reset the device to factory settings.
Step 5: Explore the Admin Interface
After logging in, you can:
- Configure Wi-Fi SSID and password
- Enable or disable guest networks
- Set parental controls
- Monitor connected devices
4. Common Uses of 192.168.l00.1
Routers use addresses like 192.168.l00.1 for multiple purposes:
- Network Configuration: Change Wi-Fi name, password, and encryption type.
- Firmware Updates: Improve security and device performance.
- Device Monitoring: View connected devices and bandwidth usage.
- Port Forwarding: Support gaming, streaming, or remote desktop applications.
- Parental Controls: Restrict content and schedule internet access for devices.
Using 192.168.l00.1 effectively requires understanding both your router and the network devices connected to it.
5. Troubleshooting 192.168.l00.1 Access Issues
Sometimes accessing 192.168.l00.1 can be challenging. Common issues include:
- Incorrect IP Address: Typographical errors, such as confusing “L” and “1” or “0”.
- Device Connectivity Issues: Ensure your device is on the same network.
- Firewall or Antivirus Blocks: Some security software may prevent access.
- Router Misconfiguration: The default IP might have been changed manually.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Ping the IP Address:
ping 192.168.l00.1If no response is received, the router may be offline or the IP incorrect. - Check IP Configuration: On Windows:
ipconfigVerify the default gateway matches 192.168.l00.1. - Reset the Router: If all else fails, a factory reset restores the default IP and login credentials.
6. Advanced Configuration via 192.168.l00.1
Beyond basic settings, 192.168.l00.1 allows advanced users to manage their networks in depth:
- QoS (Quality of Service): Prioritize bandwidth for gaming or streaming.
- Static IP Assignment: Assign fixed IPs to devices for stable connections.
- VLANs (Virtual LANs): Segment network traffic for security or performance.
- Port Forwarding and DMZ: Enable external access for specific applications or devices.
Advanced configuration requires careful attention to avoid disrupting the network. Always document changes and test connectivity after adjustments.
7. DHCP, NAT, and IP Management
Routers use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign IPs automatically to devices (check out this guide). When accessing 192.168.l00.1, you can manage:
- DHCP Range: Define which IPs the router can assign dynamically.
- Static IPs: Reserve specific IPs for devices that require consistent addresses.
- NAT (Network Address Translation): Translate private IPs for internet communication.
Proper IP management ensures efficient network performance and prevents conflicts between devices.
8. Router Firmware and Security Updates
Regular firmware updates improve security and stability, according to HP. When logged in via 192.168.l00.1:
- Check Firmware Version: Compare with the manufacturer’s website.
- Download and Install Updates: Follow the router’s update process.
- Restart Router: Ensure updates take effect.
Firmware updates fix vulnerabilities and enhance features like improved bandwidth management, VPN support, and enhanced parental controls.
9. Case Studies: Practical Uses of 192.168.l00.1
Home Network Optimization
A user experiencing Wi-Fi dead zones accessed their router via 192.168.l00.1 and enabled dual-band SSID, resulting in a 30% increase in network speed and coverage.
Small Office Network Setup
A small office used 192.168.l00.1 to set up static IPs for printers and NAS devices, ensuring reliable communication without IP conflicts.
Port Forwarding for Remote Access
A gaming enthusiast configured port forwarding through 192.168.l00.1, enabling remote access to their gaming server without downtime or connectivity issues.
These scenarios demonstrate the versatility and necessity of properly accessing the router interface.
10. Best Practices for Network Security
When managing networks via 192.168.l00.1, security is paramount:
- Change Default Credentials: Avoid common usernames and passwords.
- Enable WPA3/WPA2 Encryption: Secure your Wi-Fi network.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Patch vulnerabilities promptly.
- Monitor Devices: Detect unauthorized connections early.
- Use Strong Passwords: Include uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols.
Network security ensures a safe, uninterrupted experience for all connected devices.
11. Conclusion
192.168.l00.1 may initially appear as a typographical anomaly, but understanding its purpose and functionality is crucial for network management. From basic Wi-Fi configuration to advanced IP management, accessing this address allows users to maintain secure, efficient, and reliable networks.
Always double-check the IP address, maintain firmware and security updates, and follow best practices for network administration. Properly leveraging 192.168.l00.1 empowers both home and office users to optimize connectivity and protect their networks from threats.
FAQ
1. What is 192.168.1.1?
192.168.1.1 is a default IP address commonly used for routers. An IP address consists of four sets of numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255. The first three sets represent the network ID, and the last set identifies the specific device on that network. In the case of 192.168.1.1, the network ID is 192.168.1, and the device ID is 1.
2. How do I log in to 192.168.1.1?
To log in:
- Type 192.168.1.1 into your browser’s address bar.
- Enter your username and password.
- Click OK or Login.
3. What are the most common default login credentials for 192.168.1.1?
The most common default login credentials are:
- Username: admin
- Password: admin
4. What is the default username for 192.168.1.1?
The default username is usually admin.
5. What is the default password for 192.168.1.1?
The default password is usually admin.
6. How do I access the router’s IP address 192.168.1.1?
- Open your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the address bar.
- Enter your username and password, then click OK or Login.
Default credentials are usually: username: admin, password: admin.
7. Alternative ways to log in or use 192.168.1.1
You can access the router by typing 192.168.1.1 into your browser, then entering your username and password. The most common default credentials are: username: admin, password: admin.
